Managing business spend sounds simple, but in reality, it’s often messy. From raising purchase requests to making final payments, every handoff carries the risk of delays, errors, or compliance gaps. This is where the Procure-to-Pay (P2P) process comes in, a structured workflow that connects procurement with finance, ensuring goods and services are purchased, received, and paid for efficiently.
For modern businesses, mastering the P2P cycle isn’t just about keeping vendors happy; it’s about driving cost efficiency, improving visibility, and maintaining control over every transaction.
In this guide, we’ll break down what the P2P process is, how it works step by step, the role of automation, and even how to explain it in interviews.
What Is the Procure to Pay Process?
The Procure-to-Pay (P2P) process, sometimes simply called the P2P cycle, is the end-to-end workflow that covers everything from raising a purchase request to making the final vendor payment. In short, it connects two critical functions of any business: procurement (sourcing the right goods and services) and finance (ensuring timely, accurate payments).
Think of P2P as the bridge that keeps purchasing and accounting in sync. When done right, it reduces errors, avoids duplicate or late payments, and builds stronger supplier relationships.
For example, A retail brand needs fabric for its new collection. The buying team raises a purchase order, the vendor supplies the fabric with an invoice, the warehouse confirms receipt, and finally, finance clears the payment. That’s the P2P cycle in action, streamlined, transparent, and efficient.
Key Steps in the P2P Cycle (Step-by-Step Guide)
The procure-to-pay process flow may sound straightforward, but it involves several interconnected steps that ensure accuracy, compliance, and financial control. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the P2P cycle:
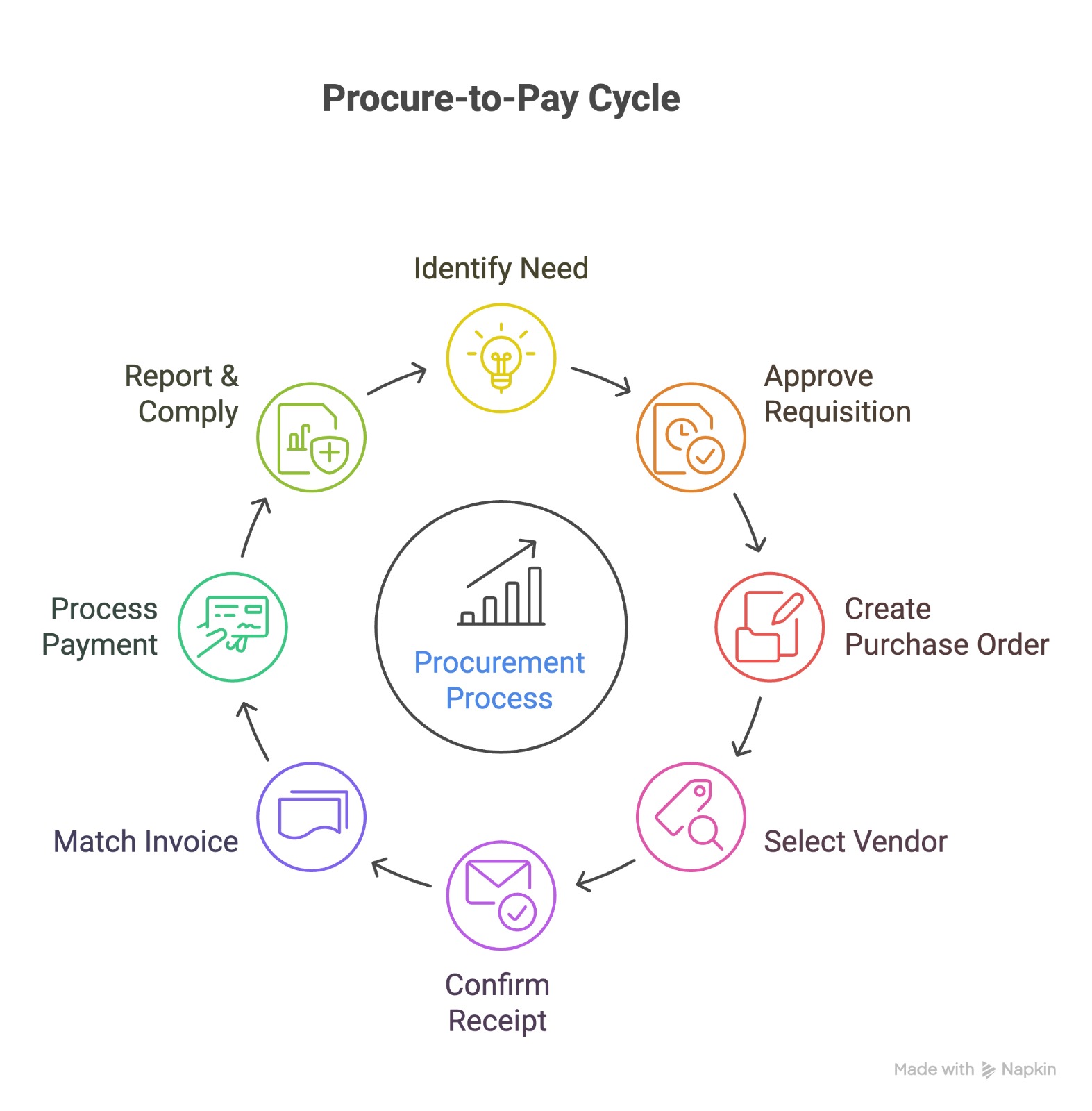
1. Identifying the Need / Requisition
Every procure-to-pay (P2P) cycle begins with recognizing a business need. This could be raw materials for production, laptops for new hires, packaging supplies, or outsourced services. The goal here is simple: to capture requirements accurately before the procurement team takes action.
A purchase requisition is raised, typically by the department that needs the item, detailing:
• What is needed (product/service specifications)
• Quantity required
• Delivery timeline
• Estimated budget
When this step is handled properly, it prevents unnecessary purchases and ensures procurement teams only engage with genuine, well-documented requests.
Example: A retail brand planning its festive season sales may raise a requisition for additional packaging materials weeks in advance, ensuring stockouts don’t disrupt timely deliveries.
2. Purchase Requisition Approval
Once a purchase requisition is raised, it moves to the approval stage, where managers or finance teams verify the request against budgets, policies, and actual business need. This step ensures that only valid and cost-justified purchases move forward, keeping spending under control.
Approval can involve one or multiple levels of authorization depending on the organization’s size and hierarchy. For example, a department head might approve small purchases, while higher-value requisitions require CFO-level sign-off.
Handled efficiently, this step prevents fraud, duplicate requests, and unnecessary spending — but when done manually, it often slows procurement with email back-and-forths and paper trails.
Example: A manufacturing company may require the operations manager’s sign-off on spare parts, but large equipment orders need approval from both procurement and finance.
3. Purchase Order Creation
After approval, the purchase requisition transforms into a Purchase Order (PO), the official document shared with the supplier. This step is crucial because it sets the foundation for delivery, payment, and accountability. A well-structured PO eliminates ambiguity and protects both buyer and supplier.
Key elements of a Purchase Order:
• Item Details & Quantity – Clearly defines what is being ordered.
• Pricing & Terms – Locks agreed costs and payment conditions.
• Delivery Schedule – Ensures suppliers meet timelines.
• Compliance Clauses – Covers warranties, returns, or regulatory needs.
Pro Tip: Automating PO creation within a P2P system speeds up approvals, reduces manual effort, and builds a reliable audit trail.
4. Vendor Selection & Confirmation
Once a purchase order is drafted, the next critical step is choosing the right vendor. A wrong choice can mean delayed deliveries, poor quality, or cost overruns, directly impacting your bottom line. This stage ensures that the organization partners with suppliers who are reliable, cost-effective, and aligned with compliance standards.
Factors considered during vendor selection:
• Quality & Reliability – Does the vendor consistently deliver what they promise?
• Pricing Competitiveness – Are they cost-effective without compromising quality?
• Capacity & Timeliness – Can they handle demand fluctuations and urgent orders?
• Compliance & Certifications – Do they meet industry regulations and company policies?
Once the vendor is shortlisted and confirmed, the PO is formally shared, locking in the agreement. Modern P2P solutions streamline this by maintaining vendor scorecards, tracking performance history, and even automating vendor comparisons.
Pro Insight: Strong vendor relationships often reduce lead times and give buyers better negotiation power for future orders.
5. Goods Receipt / Service Confirmation
After a vendor delivers goods or completes a service, the receiving team must verify that everything matches the purchase order. This is a checkpoint of accuracy — ensuring businesses only pay for what they actually receive.
Key activities during this stage include:
• Quantity Check – Does the number of items match the PO?
• Quality Inspection – Are products free from defects and up to agreed standards?
• Documentation – A Goods Receipt Note (GRN) or Service Confirmation Report is generated for records.
• Exception Handling – Any mismatch, short supply, or quality issue is flagged for resolution before moving forward.
In a manual setup, these checks often cause delays and errors. But with modern P2P systems, technologies like RFID and barcode scanning ensure real-time validation, reducing discrepancies and speeding up the approval-to-payment cycle.
Expert Tip: Always integrate GRN with your ERP/P2P platform. It ensures that only verified deliveries move ahead to invoicing, protecting your business from accidental overpayments.
6. Invoice Capture & Matching
Once goods are received, the vendor submits an invoice for payment. At this stage, the finance or procurement team verifies the invoice against the purchase order and the goods receipt, a process known as three-way matching. This ensures that the company only pays for what was actually ordered and received, preventing duplicate or fraudulent invoices.
In manual workflows, this step is prone to delays and human errors, but with automated P2P systems, invoices are digitally captured, matched in real time, and flagged instantly if discrepancies are found. This speeds up approvals, reduces disputes, and builds stronger vendor relationships.
7. Payment Processing
Once invoices are verified, payment is released to the vendor based on the agreed terms, whether immediate, within 30 days, or tied to specific milestones. Timely payments not only keep suppliers satisfied but also strengthen business relationships and open doors to better negotiation opportunities.
Key Highlights:
• Automated P2P systems eliminate bottlenecks and ensure payments are always on schedule.
• Accuracy in payment avoids late fees, penalties, or duplicate transactions.
• Consistent, timely payments build long-term trust and reliability with suppliers.
8. Reporting & Compliance
The P2P cycle concludes with reporting and compliance checks, providing visibility into spending, approvals, and payment history. These reports help finance teams audit transactions, analyze supplier performance, and ensure adherence to company policies and regulatory requirements. Proper reporting also informs future budgeting and strategic procurement decisions.
Key Highlights:
• Audit Trails – Every transaction, from requisition to payment, is recorded for accountability.
• Spend Analysis – Helps identify cost-saving opportunities and optimize vendor contracts.
• Regulatory Compliance – Ensures adherence to internal policies and external legal standards, reducing risk.
Pro Tip: Automated P2P systems generate real-time dashboards, simplifying audits and providing actionable insights for procurement and finance leaders.
Common Challenges in the Procure to Pay Process
Even with a clearly defined procure-to-pay process, many organizations face hurdles that slow down operations and increase risk. Understanding these challenges is the first step toward automating procure to pay process and improving efficiency.
Key Challenges in the P2P Cycle:
• Manual Errors & Delays – Traditional P2P processes often rely on spreadsheets, emails, and paper approvals. This increases the likelihood of errors, missed deadlines, and slow order-to-payment cycles, reducing operational efficiency.
• Lack of Integration Between Procurement & Finance Systems – When procurement and finance systems are disconnected, data inconsistencies occur, approvals get delayed, and reporting becomes fragmented. Implementing P2P process automation bridges this gap and provides seamless data flow.
• Compliance & Fraud Risks – Without automated checks, it’s harder to enforce policies, detect duplicate invoices, or prevent unauthorized purchases. A robust P2P system ensures adherence to regulatory standards while reducing fraud risk.
• Poor Visibility into Vendor Performance – Without clear insights into supplier reliability, pricing, and delivery timelines, businesses struggle to make informed sourcing decisions. A modern procure-to-pay process flow diagram can highlight these touchpoints and track vendor performance throughout the p2p cycle.
Pro Tip: Companies that adopt P2P process automation gain end-to-end visibility, reduce errors, and strengthen vendor relationships, making the procure to pay process more strategic and efficient.
Automating the Procure to Pay Process
In the fast-paced world of fashion retail, delays or errors in procurement can directly impact product availability, seasonal launches, and revenue. This is where procure-to-pay process automation becomes a game-changer. Automating the p2p cycle reduces manual effort, ensures accuracy, and provides real-time visibility across procurement and finance teams.
Key Benefits in Action:
• Faster Approvals: Requisitions for fabrics, packaging, or promotional materials are automatically routed to the right approvers, reducing bottlenecks.
• Fewer Errors: Digital invoice matching ensures payment is only made for received goods, avoiding overpayments or duplicate invoices.
• Compliance Tracking: Automated checks enforce internal policies and audit trails, reducing the risk of compliance issues.
• Cost Savings: Optimized vendor selection, reduced processing time, and fewer errors help control costs and improve margins.
Use Case Example – Fashion Retail:
A fashion brand preparing for its festive season collection needs to procure hundreds of garment components and packaging materials across multiple vendors. By automating its p2p process, the brand generates POs directly from approved requisitions, tracks deliveries in real time, and matches invoices automatically against purchase orders and goods receipts.
The system flags any discrepancies instantly, ensuring timely payments only for verified deliveries. Meanwhile, the brand monitors supplier performance and overall spend, allowing procurement and finance teams to make informed decisions quickly. The outcome: faster procurement cycles, minimal errors, better vendor relationships, and on-time product launches.
Why the Procure to Pay Process Matters for Businesses
• Cost Savings: Efficient procurement reduces unnecessary spending, prevents duplicate orders, and ensures accurate payments. Companies can negotiate better pricing and optimize their overall spend.
• Better Vendor Relationships: Timely orders and consistent payments strengthen trust with suppliers, enabling more favorable terms, faster deliveries, and reliable partnerships.
• Improved Compliance & Audit Readiness: Every step of the P2P process is documented, creating audit trails and enforcing adherence to internal policies and regulatory requirements. This minimizes risk and ensures financial transparency.
• Stronger Cash Flow Management: By tracking purchase commitments, invoice approvals, and scheduled payments, businesses gain better visibility into cash flow, enabling smarter financial planning and liquidity management.
Final Thoughts
The procure to pay process is more than just a series of operational steps — it’s the backbone of procurement and finance, ensuring accuracy, compliance, and financial control across the organization. From requisition to payment, a well-managed p2p cycle drives cost efficiency, strengthens vendor relationships, and provides actionable insights for smarter business decisions.
In today’s fast-moving business environment, adopting procure to pay process automation is no longer optional. Automation accelerates approvals, reduces errors, ensures compliance, and gives teams the visibility they need to scale operations effectively.
Looking to automate your procure-to-pay process? Explore how DigiProc simplifies the P2P cycle for modern enterprises. Book a demo
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does the procure-to-pay process impact cash flow management?
An efficient P2P process helps organizations manage their cash flow by ensuring timely payments to suppliers and avoiding late fees. By automating invoice approvals and payment scheduling, businesses can maintain a steady cash flow and strengthen supplier relationships.
2. Why is vendor selection crucial in the P2P cycle?
Selecting the right vendor is vital as it directly affects the quality of goods or services received, delivery timelines, and overall cost-effectiveness. A thorough evaluation process ensures that the chosen supplier aligns with the organization’s requirements and standards.
3. What is a three-way match in the P2P process?
A three-way match involves comparing the purchase order, goods receipt note, and supplier invoice to ensure consistency among all documents before processing payment. This practice helps prevent discrepancies, overpayments, and fraud.
4. How can businesses ensure compliance in the P2P process?
Implementing automated workflows, setting up approval hierarchies, and integrating procurement systems with finance can help enforce compliance. Regular audits and monitoring also play a crucial role in maintaining adherence to internal policies and external regulations.
5. What are the benefits of integrating procurement and finance systems?
Integration between procurement and finance systems facilitates seamless data flow, reduces manual data entry, enhances accuracy, and provides real-time visibility into spending and budget adherence. This alignment leads to more informed decision-making and improved operational efficiency.
