Vendor selection is harder than ever as businesses manage complex supply chains, new technologies, and rising compliance demands. Studies show 58% of organizations use RFIs to improve early vendor evaluation, and adoption of digital RFI processes is growing 12–15% annually.
An RFI (Request for Information) helps companies gather structured details about a vendor’s capabilities, experience, and technical or compliance fit before moving to proposals or pricing. This early clarity reduces risk, speeds up procurement, and ensures only qualified suppliers advance to RFP or RFQ stages.
This guide explains RFI meaning, process, templates, components, and best practices to help you create effective RFIs.
What Is a Request for Information (RFI)?
An RFI (Request for Information) is an early-stage procurement document used to collect essential information from potential vendors before evaluating proposals or pricing. Organizations use RFIs to understand whether a supplier is capable, reliable, compliant, and technically aligned with the project’s needs. It helps teams compare vendors objectively and eliminates guesswork during supplier shortlisting.
Why Use an RFI?
Before issuing an RFP or RFQ, procurement teams need clarity on:
• Who can deliver the required service or solution
• Which vendors meet technical and compliance needs
• Who is worth advancing to the next evaluation stage
RFIs reduce risk, eliminate unsuitable vendors early, and streamline the sourcing process.
How an RFI works
1. The buyer shares an RFI with multiple vendors
2. Vendors respond with details about capabilities, experience, processes, and suitability
3. The buyer uses responses to shortlist the most qualified suppliers
4. Only shortlisted vendors receive RFPs (proposals) or RFQs (pricing)
Example Scenario
A retail brand wants to evaluate new warehouse automation partners. Instead of calling every vendor, they issue an RFI asking:
• “What automation solutions do you offer?”
• “What integrations are supported?”
• “What’s your experience with multi-location retailers?”
This creates a clean, comparable set of responses, and saves weeks of confusion.
RFI vs RFP vs RFQ: What’s the Difference?
Procurement has three core evaluation documents, each serving a different stage:
| Feature | RFI (Request for Information) | RFP (Request for Proposal) | RFQ (Request for Quotation) |
| Purpose | Understand capabilities | Evaluate detailed solutions | Get final pricing |
| When Used | Early discovery stage | Mid-stage evaluation | Final decision stage |
| Detail | Low | High | Very High |
| Output | Vendor shortlist | Solution proposal | Exact pricing |
Simple way to remember
• RFI → Who can do the job?
• RFP → How will they do it?
• RFQ → How much will it cost?
Why RFIs Matter (Benefits for Procurement & Supply Chain Teams)
RFIs play a critical role in modern sourcing, and understanding the RFI meaning and purpose can significantly improve vendor evaluation. In procurement, an RFI (Request for Information) is more than an initial questionnaire, it is a strategic tool designed to reduce risk, improve clarity, and create structured insights before deeper supplier engagement. This makes the RFI process one of the most important early steps in vendor sourcing.
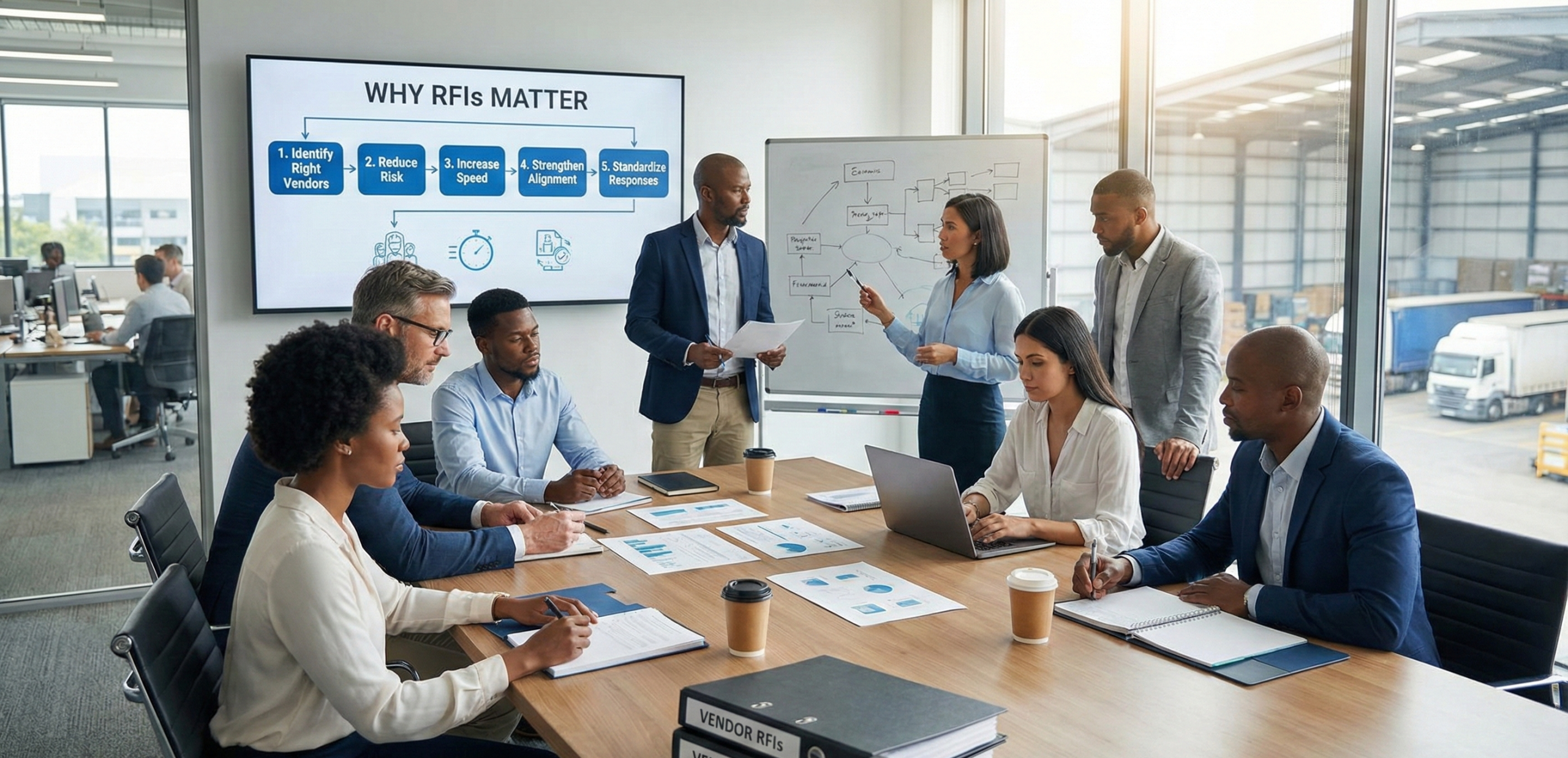

1. Identify the Right Vendors Early in the RFI Process
An RFI helps procurement teams filter vendors early by examining their capabilities, experience, and technical fit. Before investing time in proposals, RFIs quickly reveal whether a vendor aligns with project requirements. This is essential for effective RFI in procurement workflows.
2. Reduce Risk and Prevent Poor Vendor Decisions
A well-structured RFI prevents:
• Wrong technology choices
• Onboarding non-compliant suppliers
• Working with unreliable or unqualified vendors
Understanding what an RFI stands for and how it works ensures organizations avoid costly sourcing mistakes.
3. Increase Procurement Speed and Efficiency
By shortlisting only capable vendors, the RFI process eliminates unnecessary back-and-forth communication. Organizations typically reduce evaluation time by 40–60%, making RFIs one of the fastest ways to streamline sourcing.
4. Strengthen Cross-Functional Alignment
RFIs ensure that procurement, IT, operations, and finance receive the same structured vendor information. This alignment minimizes misunderstandings and improves internal decision-making, a major benefit of RFIs in complex projects.
5. Create Standardized, Comparable Vendor Responses
Instead of inconsistent emails or sales-heavy documents, RFIs enforce a fixed response format. This allows procurement teams to compare vendors objectively across:
• Technical capabilities
• Operational strengths
• Compliance
• Scalability
These structured insights lead to stronger vendor partnerships and better sourcing outcomes.
When Should a Company Use an RFI?
Companies should use an RFI (Request for Information) whenever they need structured details from vendors before making purchasing or sourcing decisions. In procurement, RFIs are most valuable during the early discovery stage, when teams are exploring the market, comparing capabilities, or trying to reduce uncertainty. Whenever knowledge gaps exist, the RFI process helps identify which suppliers are worth evaluating further.
Common use cases for RFIs
RFIs are especially useful when organizations need clarity on technology, compliance, capabilities, or vendor experience. Typical scenarios include:
• Evaluating new technology solutions
(ERP, WMS, RFID systems, automation tools, SaaS platforms)
• Shortlisting suppliers for long-term or high-value contracts
• Entering a new product category or expanding into new geographies
• Comparing operational and technical capabilities of logistics partners
(3PL, warehousing, transportation providers)
• Assessing compliance and risk requirements
(ESG, ISO certifications, data protection, industry regulations)
• Understanding vendor maturity and scalability before issuing an RFP or RFQ
Examples
• A fashion retailer exploring new fabric suppliers.
• A manufacturing company looking for 3PL warehousing partners.
• A procurement team evaluating SaaS tools for digitization.
Wherever knowledge gaps exist, an RFI fills them.
Key Components of an Effective RFI (RFI Document Format)
A strong RFI in procurement is well-structured, easy to understand, and designed to collect consistent information from all vendors. The goal is to simplify comparison and ensure suppliers respond in a uniform format. Below are the essential RFI components every organization should include in their RFI document format:
1. Company Background: Provide a brief overview of your organization, industry, and project context. This helps vendors understand who you are and align their responses accordingly.
2. Project Overview: Describe the project’s purpose, goals, challenges, and the specific problem you are trying to solve. This ensures vendors respond with relevant and meaningful information.
3. Information Requested from Vendors: Detail the exact information you need, such as:
• Capabilities
• Experience in similar projects
• Technical details
• Analytics/reporting capabilities
• Timelines and delivery expectations
This ensures you receive structured and useful responses.
4. Vendor Profile: Request basic vendor information, including:
• Years in business
• Industry expertise
• Previous clients or case studies
• Geographic coverage
• Organizational size
This helps evaluate credibility and fit.
5. Technical Requirements: Clearly outline your technical expectations, such as:
• Integrations needed
• Performance metrics
• Architecture or system compatibility
• Security standards
• Technical certifications
Including these early prevents misalignment later in the procurement process.
6. Operational Capabilities: Ask vendors about their operational strengths:
• Delivery timelines
• Capacity and scalability
• Processes and tools used
• Support structure
• Service level expectations
This helps determine if the vendor can meet your operational needs.
7. Compliance & Certifications: Request details on:
• ISO certifications
• ESG policies
• Data protection measures
• Industry-specific compliance (e.g., SOC, GDPR, safety standards)
This ensures all shortlisted vendors meet your risk and regulatory requirements.
8. Pricing Structure (High-Level): You’re not asking for exact pricing yet, only the model, such as:
• Subscription
• Licensing
• Per-unit or per-transaction pricing
• One-time implementation fees
High-level pricing helps compare financial models early in the RFI process.
9. Submission Guidelines: Provide clear instructions, including:
• Required format
• Response length
• Deadline
• Point of contact
• Submission channel (email, portal, procurement tool)
10. Evaluation Criteria (Optional but Highly Recommended): Sharing your evaluation criteria increases RFI response quality. Vendors understand what matters most, whether it’s technical fit, compliance, scalability, or cost structure.
How to Write an RFI (Step-by-Step Guide)
Step 1: Define Your Purpose
Start by clarifying why you are issuing the RFI. This ensures your questions align with the project’s objectives.
Example: “To evaluate warehouse management solutions for multi-location operations.”
Step 2: List the Information You Need
Identify what you must learn from vendors, such as:
• Capabilities
• Technology stack
• Industry experience
• Integration requirements
• Workflow and operational fit
Step 3: Draft Structured, Comparable Questions
Create questions that are clear, categorized, and standardized across all vendors. Structured questions make it easy to compare suppliers on equal terms. Use direct, objective formats (e.g., Yes/No, multiple choice, short explanations).
Step 4: Provide Detailed Response Instructions
Set expectations so vendors know exactly how to respond. Include:
• Required format (PDF, spreadsheet, portal submission, etc.)
• Response length or limits
• Submission deadline
• Point of contact for clarifications
Clear instructions reduce ambiguity and improve response quality.
Step 5: Add Qualification or Mandatory Criteria
List any non-negotiable requirements, such as:
• “Must integrate with ERP”
• “Must support RFID”
• “Must comply with ISO 27001”
Step 6: Review Internally With Stakeholders
Collaborate with teams such as procurement, IT, operations, finance, and compliance. Internal alignment ensures your RFI reflects cross-functional needs and avoids future conflicts.
Step 7: Share the RFI With Vendors
Send the finalized RFI to selected suppliers and clearly communicate the response timeline, expectations, and any scheduled Q&A sessions.
Step 8: Evaluate Responses With a Scoring Matrix
Use a predefined scoring model to compare vendors across key criteria like:
• Technical fit
• Compliance
• Experience
• Scalability
• Pricing model
A scoring matrix ensures objective, data-driven shortlisting and eliminates bias.
Sample RFI Template (Copy & Use)
Below is a universal, professionally structured RFI template that organizations can use across industries. It follows a clear RFI document format, ensures consistency, and helps vendors respond in a structured way. You can copy, customize, and use it for any procurement requirement.
RFI Template
1. Introduction: Provide a brief overview of your company, industry context, and why you are issuing this RFI. Example: “We are evaluating solutions to improve warehouse automation across multiple locations.”
2. Project Overview: Outline the project goals, scope, expected outcomes, and any challenges you aim to address. This helps vendors tailor their responses to your objectives.
3. Information Requested from Vendors: Specify what details you want vendors to provide, such as:
• Technical capabilities
• Product or service features
• Operational strengths
• Experience in similar projects
• Implementation approach
• Scalability and support
4. Vendor Questions: List all questions vendor must answer, grouped by category:
• Company Profile
• Technical Fit
• Operational Capabilities
• Implementation & Support
• Compliance
• Pricing Model
Structured questions speed up evaluation and eliminate ambiguous responses.
5. Compliance Requirements: Request details on:
• Certifications (ISO, SOC, ESG, GDPR, industry-specific)
• Data security standards
• Quality assurance processes
• Regulatory adherence
This ensures shortlisted vendors meet your compliance criteria.
6. Pricing Structure (High-Level): Ask vendors to outline their pricing model—not exact numbers. Common formats include:
• Licensing or subscription
• Usage-based pricing
• Per-unit or per-location pricing
• One-time setup or implementation fees
This section helps compare pricing approaches early in the RFI process.
7. Submission Guidelines: Provide clear instructions on:
• Required submission format
• Response structure
• Deadline for submission
• Contact person for queries
• Submission channel (portal, email, procurement tool)
Clear guidelines improve response quality and ensure faster evaluation.
Final Words
RFIs remain one of the most powerful tools in procurement. When used correctly, an RFI provides clarity, reduces risk, and ensures your organization evaluates only the most capable and compliant vendors. Whether you’re assessing new technology, onboarding suppliers, comparing logistics partners, or exploring new categories, a structured RFI process sets the foundation for smarter sourcing decisions. By using the right RFI format, structured questions, and clear evaluation criteria, companies can streamline vendor discovery, improve cross-functional alignment, and accelerate the path to RFP, RFQ, and final negotiation.
Digitize RFIs and Vendor Onboarding with Supplymint DigiProc
Looking to eliminate spreadsheets, email chains, and manual comparisons? Supplymint DigiProc helps procurement teams automate and streamline:
✔ RFI creation and distribution
✔ Vendor onboarding & document collection
✔ RFP/RFQ management
✔ Centralized vendor data
✔ Scoring, evaluation, and audit trails
✔ End-to-end procurement workflows
Upgrade your procurement process with a platform built for speed, accuracy, and compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is an RFI legally binding?
No. An RFI (Request for Information) is not legally binding. It is an exploratory document used only to gather information. No contractual obligations or commitments are created for either party.
2. Who typically prepares an RFI in a company?
RFIs are usually created by procurement teams, but in many organizations, IT, operations, finance, engineering, or project management teams collaborate to define requirements and questions.
3. How long should an RFI take for vendors to complete?
Most RFIs take 3–10 business days depending on complexity. Companies should balance detail with efficiency, overly long RFIs discourage vendor participation.
4. How many vendors should receive an RFI?
Typically between 5–12 vendors. Sending an RFI to too few suppliers limits competition; sending to too many creates unnecessary evaluation workload.
5. What’s the difference between an RFI response and a proposal?
An RFI response provides general information, capabilities, and qualifications. A proposal (RFP) includes detailed solutions, pricing, timelines, and contractual details.