In the world of procurement, supply chain management, and financial analysis, tracking costs is essential to maintaining profitability. One key metric that helps businesses understand the fluctuations in their purchasing costs is Purchase Price Variance (PPV). But what exactly is PPV, and why should businesses care about it?
In this blog, we’ll explore the meaning of PPV, its formula, how to calculate it, and the importance of this variance in the procurement process. Additionally, we will highlight how businesses can leverage PPV data to improve purchasing decisions and ultimately strengthen their financial position.
What Is PPV (Purchase Price Variance)?
Purchase Price Variance (PPV) refers to the difference between the actual price paid for a good or service and its expected or standard price. This variance plays a crucial role in financial analysis and procurement management, helping businesses track discrepancies between the forecasted cost and the actual cost of purchases. By understanding PPV, companies can better manage procurement budgets, evaluate supplier performance, and make informed decisions.
Types of PPV
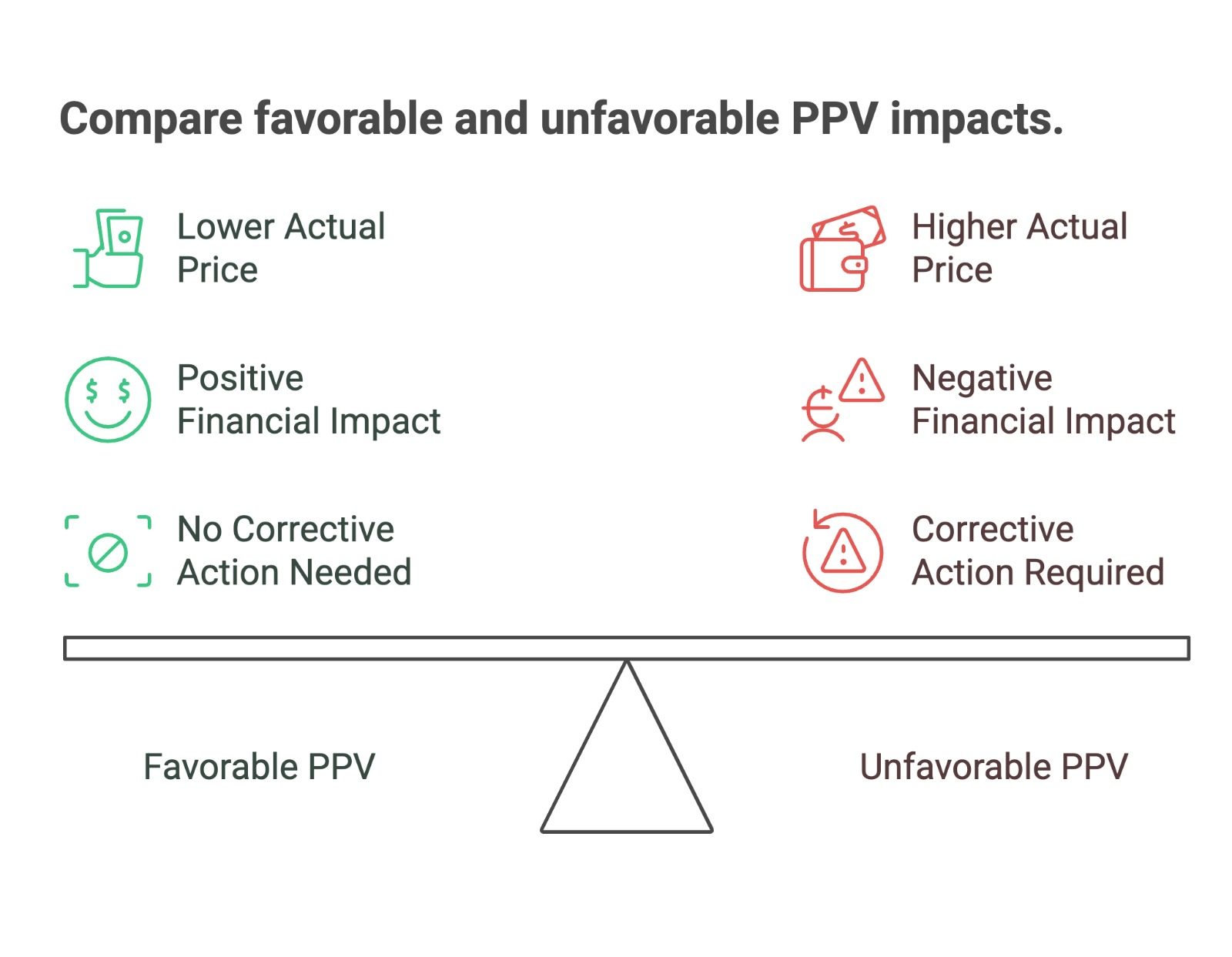
1. Favorable PPV: A favorable variance occurs when the actual price paid is lower than the standard price. This scenario can result from discounts, better-than-expected negotiations, or a favorable market shift. A favorable PPV contributes positively to a company’s financial health.
2. Unfavorable PPV: An unfavorable variance arises when the actual price paid is higher than the standard price. This situation might be caused by rising raw material costs, vendor price hikes, or other unexpected supply chain disruptions. While unfavorable PPV can affect profit margins, identifying it early allows businesses to take corrective action.
The Formula for Purchase Price Variance
Understanding how to calculate PPV is crucial for financial analysts and procurement managers. The formula is relatively simple but requires accurate data to be effective:
PPV = (Actual Price – Standard Price) × Actual Quantity
Where:
• Actual Price is the price paid per unit of the product or service.
• Standard Price is the predetermined or expected price for the product or service, often based on historical data or budgeted costs.
• Actual Quantity is the number of units purchased.
Example of PPV Calculation
Let’s walk through a simple example to better understand how to calculate PPV.
Imagine a company that purchases 1,000 units of a raw material, and the standard price is set at $10 per unit. However, due to a supplier price increase, the actual price paid is $12 per unit.
Using the formula:
PPV = (Actual Price – Standard Price) × Actual Quantity
PPV = ($12 – $10) × 1,000
PPV = $2 × 1,000 = $2,000 (Unfavorable PPV)
In this case, the company spent $2,000 more than expected, which means the PPV is unfavorable.
Conversely, if the actual price paid had been $8 per unit, the PPV would have been favorable.
How to Calculate Purchase Price Variance
The calculation of PPV may seem simple on the surface, but it’s important to ensure the data is accurate. Let’s break down the process further:
1. Identify the Standard Price: This is typically determined during the budgeting process and represents the expected price for goods or services. Companies may rely on historical purchasing data, market analysis, and supplier contracts to set this figure.
2. Determine the Actual Price: The actual price is the price the company actually paid for the goods or services. This is recorded at the point of purchase, factoring in any discounts, price changes, or additional charges from the supplier.
3. Record the Actual Quantity: The actual quantity refers to the number of units purchased. This information is usually recorded in the purchasing system, and it’s important to use the correct number to ensure the PPV calculation is accurate.
4. Apply the PPV Formula: Finally, apply the formula to calculate the variance. The result will show whether the company is spending more or less than planned, and by how much.
A Quick Example for Better Understanding
Let’s say a company forecasts the purchase of 5,000 units of a component at $20 each. However, due to a shortage in supply, the company ends up purchasing only 4,000 units at $25 each.
• Standard Price: $20
• Actual Price: $25
• Actual Quantity: 4,000
PPV = (25 – 20) × 4,000 = $5 × 4,000 = $20,000 (Unfavorable PPV)
In this case, the company spent $20,000 more than expected, indicating a significant unfavorable PPV. This would require analysis to determine the root cause and assess any potential corrective actions.
Why Is Purchase Price Variance Important?
1. Budgeting and Cost Management
By regularly calculating PPV, companies can better control costs and adjust budgets based on actual performance. If unfavorable variances are frequent, it may indicate the need for renegotiating contracts with suppliers or finding alternative sourcing strategies.
2. Supplier Performance Evaluation
Tracking PPV is an effective way to evaluate supplier performance. If a supplier consistently provides goods at a higher price than expected, it could be a sign of inefficiency or price volatility that needs addressing. Conversely, favorable PPV could indicate a reliable and cost-effective supplier.
3. Identifying Cost Drivers
Analyzing PPV allows businesses to identify cost drivers—specific factors that contribute to price fluctuations. Whether it’s supply chain disruptions, changes in market conditions, or vendor pricing strategies, knowing the root cause of PPV can help companies take proactive steps to mitigate future cost increases.
4. Profitability Insights
PPV has a direct impact on profitability. Unfavorable PPV erodes profit margins, while favorable PPV boosts them. By monitoring PPV, businesses can gain insights into how purchasing decisions are affecting their bottom line and take action to ensure sustained profitability.
How PPV Impacts Supply Chain Operations
PPV plays a pivotal role in optimizing supply chain operations. When purchasing costs deviate from expectations, it can lead to inefficiencies in inventory management, demand forecasting, and cash flow planning. Here’s how:
• Inventory Management: If the actual price paid for goods is higher than anticipated, it could affect how much inventory the company can afford to stock. Unfavorable PPV may force businesses to adjust their inventory levels or seek alternative sourcing options.
• Demand Forecasting: PPV can help refine demand forecasting models. By understanding how price fluctuations impact purchasing decisions, businesses can adjust their forecasts to reflect real-world conditions more accurately.
• Cash Flow Planning: Supply chain operations are often constrained by cash flow. Unfavorable PPV can strain cash flow, requiring businesses to find ways to adjust their purchasing practices or seek financing options to cover the additional costs.
How to Minimize PPV
While some level of variance is inevitable, businesses can take steps to minimize PPV by adopting best practices in procurement and supplier management:
1. Negotiating Fixed Prices: Whenever possible, negotiate long-term contracts with suppliers that lock in prices for an extended period. This reduces the risk of sudden price hikes.
2. Maintaining Strong Supplier Relationships: Establishing close relationships with suppliers can lead to better deals, discounts, and more favorable terms, thus helping to keep PPV within acceptable limits.
3. Using Technology: Implement procurement management software like SupplyMint to track purchasing trends and identify early warning signs of unfavorable PPV. Automation tools can also help optimize the procurement process.
4. Monitoring Market Conditions: Regularly monitor the market to stay aware of potential cost increases, such as changes in raw material prices or geopolitical disruptions. This proactive approach can help you adjust your purchasing strategy before unfavorable PPV occurs.
Conclusion
Purchase Price Variance (PPV) is a crucial metric that provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of a company’s procurement strategy. By calculating PPV and understanding its significance, businesses can make more informed purchasing decisions, control costs, and improve their financial performance. Monitoring PPV also allows companies to assess supplier relationships and take corrective actions when necessary.
At SupplyMint, we understand the importance of optimizing procurement and minimizing costs. Our advanced tools can help you track PPV, streamline purchasing processes, and make data-driven decisions to keep your business profitable. Explore our powerful procurement solutions that help businesses like yours stay ahead in a competitive market.
